Ruby Exam: Exceptions
This article covers Ruby exceptions that frequently appear in the Ruby Silver certification exam.
Execution Order
Wrap code that may raise an exception with begin and end, and handle exceptions with rescue inside that block.
begin # Executed if no exception occurs
↓
rescue # Executed if an exception occurs in the begin block ↔︎ Not executed if no exception occurs
↓
else # Executed if the rescue block was not executed ↔︎ Not executed if the rescue block was executed
↓
ensure # Always executed
Example
begin
1 / 0
p 1
rescue # `begin`節が実行されなかったので、`rescue`節が実行される
p 0
else
p 2
ensure # 必ず実行される
p 3
end
=> 0, 3
begin # `begin`節が実行
p 1
rescue
p 0
else # `rescue`節が実行されなかったので、`else`節が実行される
p 2
ensure # 必ず実行される
p 3
end
=> 1,2,3
Exception Class Hierarchy
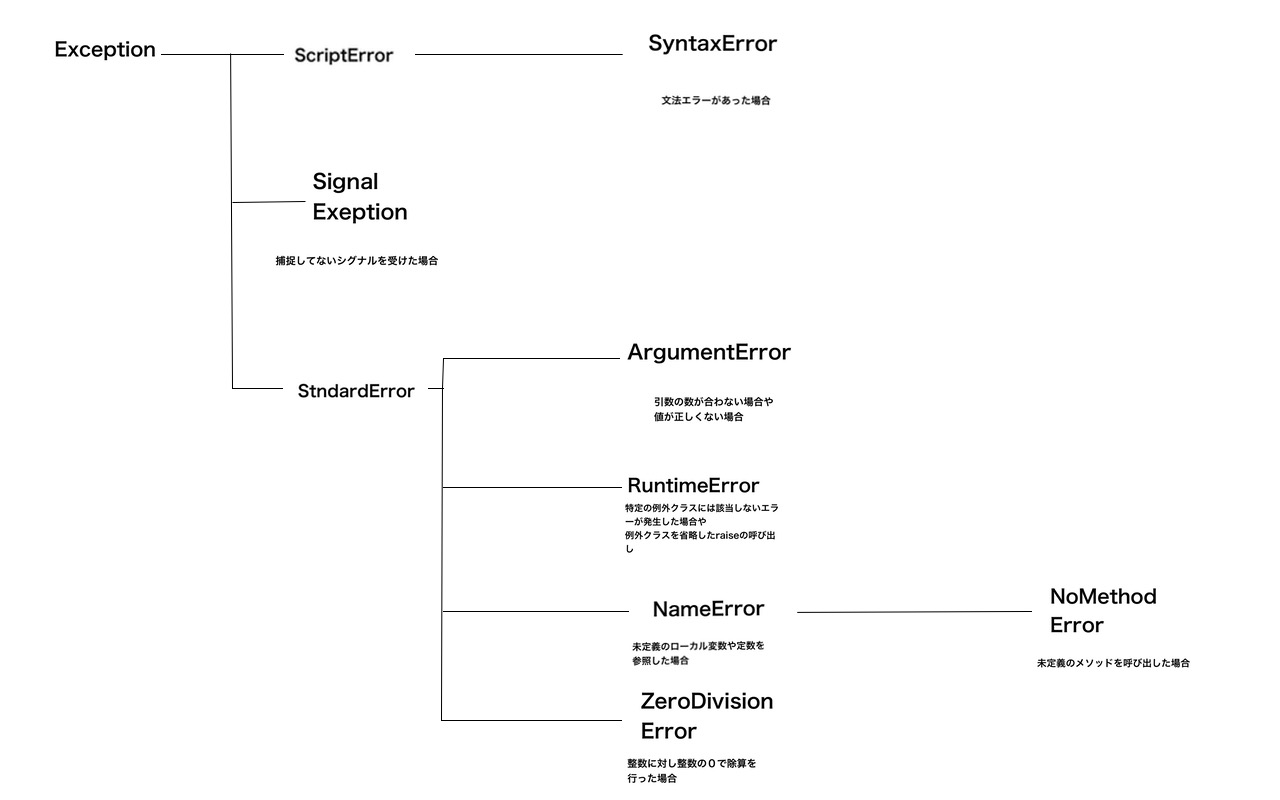
If you specify an identifier after the exception class with =>, you can reference the exception object.
message method → The specified exception message
backtrace method → Reference the location where the exception occurred
# `message method` → The specified exception message
begin
# Intentionally cause an exception
10 + nil
# Assign the exception object to the variable error
rescue => error
# Display the error message
puts error.message
end
=> nil can't be coerced into Integer
# `backtrace method` → Reference the location where the exception occurred
begin
# Intentionally cause an exception
10 + nil
# Assign the exception object to the variable error
rescue => error
# Display the error backtrace
puts error.backtrace
end
=> exam.rb:3:in `+'
exam.rb:3:in `<main>'
retry
retry is used in the rescue block to execute the begin expression again from the start. By using retry, you can create a loop that repeats a process until it succeeds. The ensure block is executed only once.
a = 0
begin
b = 1 / a
rescue ZeroDivisionError
a += 1
retry
ensure
p b
end
=> 1
Notes on rescue blocks
You can specify multiple rescue blocks within a single begin block. However, only the first matching one will be executed.
Reference
